INDIAS STRATEGIC COASTLINE
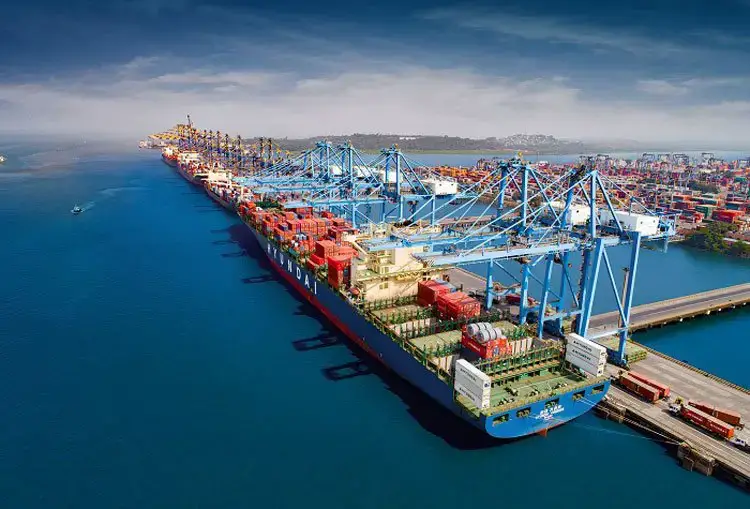


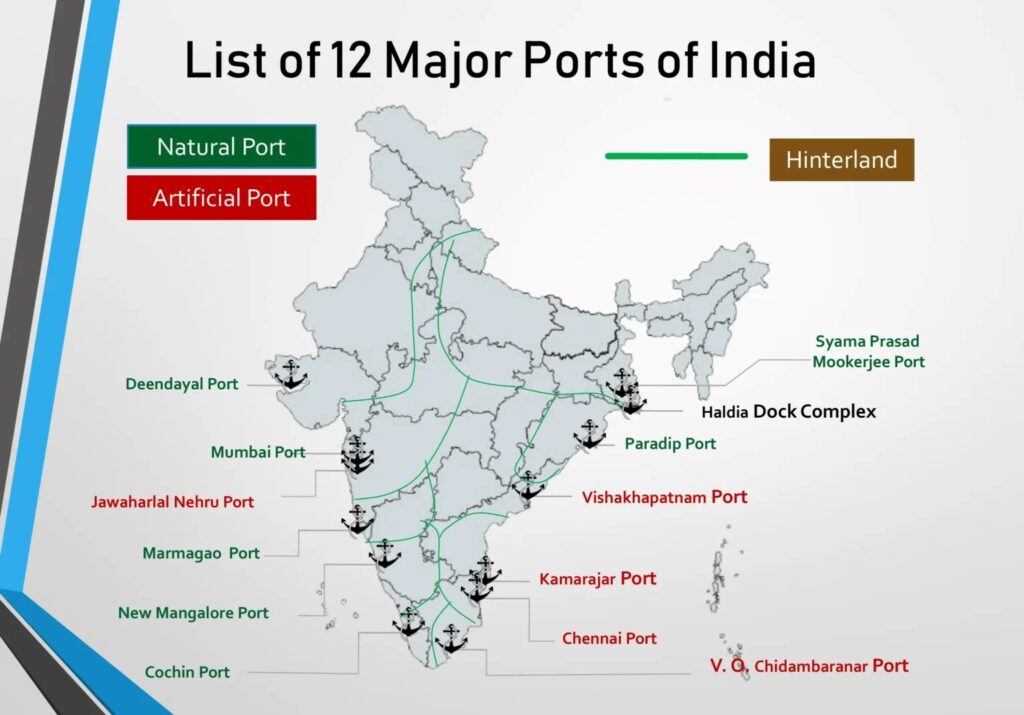
India, with a strategically located coastline extending for more than 7,500 kms and 13 major seaports, is highly reliant on maritime trade. Seaports play an essential role in the Indian economy, acting as entry points for international commerce and centers for the transfer of goods and merchandise.

The 11th biennial international conference on ports, shipping and logistics 2023 was held in Mumbai, the theme, “Envisioning the Future of Logistics @2047”, organized by Bombay Chamber of Commerce and Industry (BCCI). The conference was attended by industry leaders, policy makers and investors and focused on the critical role of an integrated and agile logistics ecosystem in transforming India into a world-class trading power by 2047.
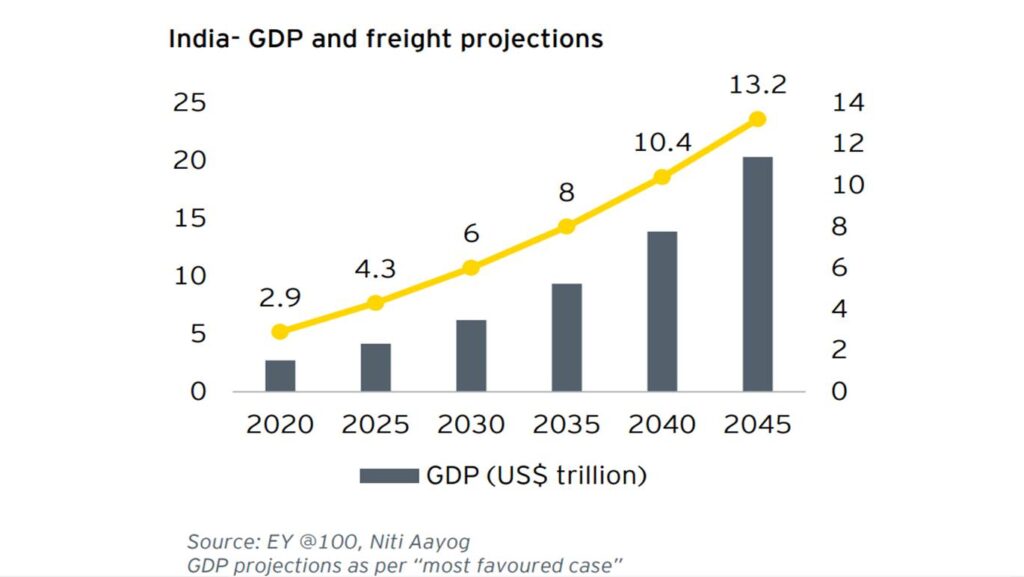
India is expected to grow to a US$26 trillion economy by FY48, according to a recent EY report titled “India@100: Realizing the Potential of a US$ 26 T economy.”. India’s transportation and logistics industry can serve as the foundation for the nation’s anticipated rapid growth over the next 25 years. The logistics industry is projected to experience a 10-12% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in the near future due to policy developments and infrastructure upgrades, thus enhancing India’s competitive edge. With a surge in demand, the logistics market, currently estimated at ~$250 billion, is projected to expand at a CAGR of 10-12% to reach $380 billion by FY25.

In his welcome speech, President of Chamber Nilesh Shah who is also Managing Director (MD) of KMT Asset Management Co Ltd stressed on the importance of the Chamber as a bridge between the corporate world and the government.

Nitin Gadkari, Union minister for Road Transport and Highways was the chief guest of honor and stressed upon his principle four E’s that are crucial to streamline the ports, shipping and logistics industry in India and said, “I would list four Es necessary to streamline the sector: Ethics, Economy, Ecology and Environment. Environment is of the highest priority. It is time to encourage public transport and the use of Green fuels like ethanol, methanol and green hydrogen.”
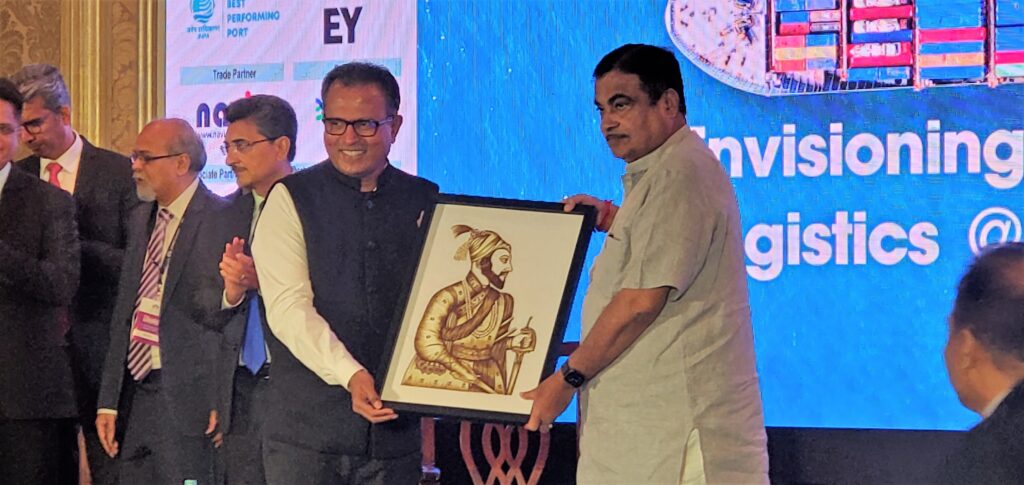

Mr. Gadkari updated of the progress of the infrastructure projects currently underway, most of the work of the Delhi Mumbai expressway will be completed by December 2023, and shared that about 7 to 8 logistics parks will be set up in Maharashtra along with dry ports in Pune, Nashik, Mumbai and Nagpur. “We are also planning to develop Busports on the lines of airports. Besides, 40 river ports are also planned including Varanasi and Sahibganj,” he stated. He further stated that the construction of two dry ports in the state of Maharashtra, located in the Jalna river and the Wardha river, had been completed and that the development of two more dry ports, located in the Nashik river and the Pune river, was underway. The Union government has made ecology and the environment a top priority and is exploring various strategies to reduce pollution, the Minister stated, adding that various projects are being pursued on a war-like basis.
The importance of public transport in the country cannot be overstated. Approximately 40% of the country’s total air pollution is attributed to road transport, thus necessitating the implementation of public transport, which the government is currently undertaking.
The government also intends to construct an electric highway, or e-highway, he said. He added that electric buses and electric cars, as well as electric scooters, are already in operation. We are also beginning to use flex engines in our vehicles, he said. “Hydrogen is the future fuel,” he said.

The Mumbai-Goa Highway Project was delayed due to a variety of reasons, all of which have been rectified and approximately 73% of the work has been completed. The Director of the project expressed his assurance that the project will be completed on schedule.
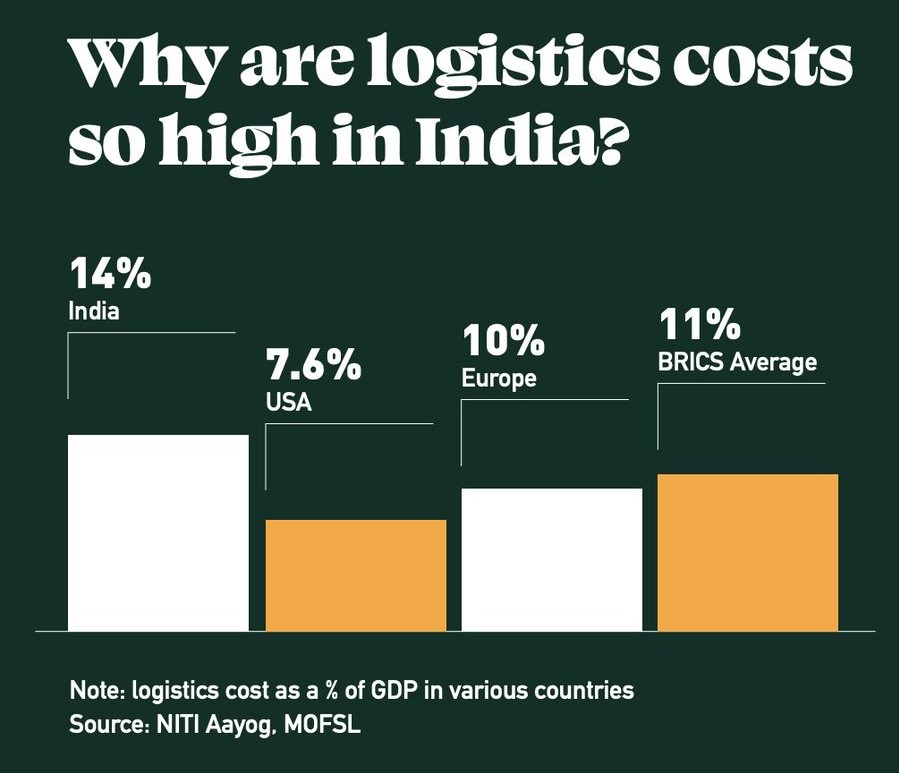
The government is striving to reduce logistics costs to 9% by 2024, as opposed to the current rate of 14-16%. He asserted that improved roads and reduced logistics costs would lead to increased business and industrial growth. It is estimated that a 10% reduction in indirect logistics cost will result in 5% to 8% rise in exports. He disclosed the work on 36 green highway projects has commenced. Through the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan (NMP), the logistics expenses will be cut to 9% of GDP, as the higher logistics costs make the “Made in India” items less competitive in international markets.
GoI has initiated a number of initiatives to promote the construction of new infrastructure, including roads, railways, ports, and more. Additionally, initiatives are being taken to facilitate the recruitment of private capital and administrative reforms to facilitate the planning and implementation of infrastructure investments. India’s new logistics policy, The National Logistics Policy (NLP), is aimed at promoting the seamless movement of goods and enhancing the global competitiveness of Indian industry.

The Minister further asserted that the introduction of waterborne transport services between the cities of Mumbai and Goa would have a significant impact on the transport landscape of the region. Additionally, the Minister stated that the government is conducting research into road engineering in order to reduce the number of road accidents and their associated damages.
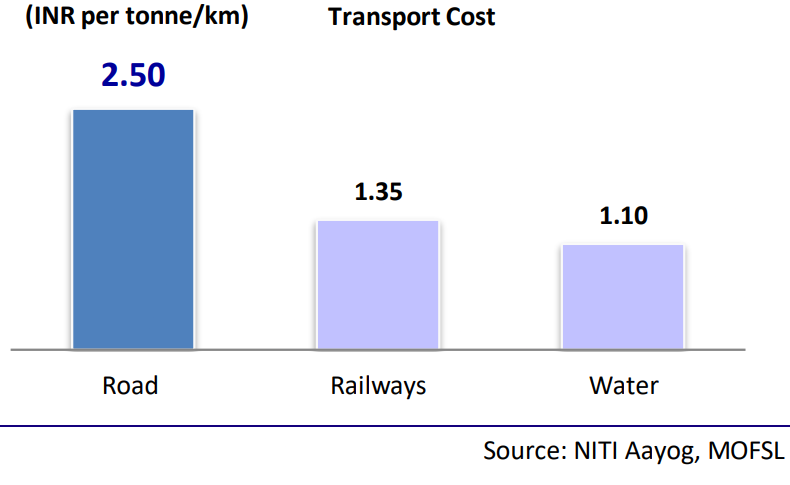
India’s freight movement is highly concentrated on road, which carries 66% of the cargo (ton-km), followed by rail with 31%, shipping with 3% and air with 1%. The sector continues to experience discrepancies in freight transportation modes and is working to overcome this issue.

At the 11th biennial international conference on ports, shipping and logistics 2023, Ernst & Young released the latest thought leadership report, “Envisioning the future of Indian logistics@2047”.
Mr. Neveille Dumasia in his speech, traditionally, the Indian government has been the chief proponent and financier of infrastructure development. However, it is increasingly adopting new policies to attract private and foreign investment as levers to fast-track infrastructure development. The National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) is one such lever that is expected to raise INR 50 lakh crore (approximately US$650 billion) worth of investment. Although 100% FDI is allowed in most transport infrastructure development initiatives, considerable effort will be needed to bring about the desired impact.

India’s shipping and logistics sector is aligning with domestic and global regulations on sustainable practices as well. The sector is taking steps to conform with leading global benchmarks such as Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index, Carbon Intensity Rating, and Emissions Trading System.
Neville M Dumasia, National Leader – Advanced Manufacturing, Mobility and Infrastructure, EY India.

Mr. Shripad Naik, Minister of state for Ports, Shipping and Waterways, Government of India addressed the conference and emphasized the importance of PPP in the shipping industry. “India’s geographic location makes it an important transit hub for the global shipping industry. Public Private Partnership (PPP) will play an important role in the growth of the maritime sector in India and an important source of investment as well.”

Speaking at the conference, Anil Radhakrishnan, Chairman – Expert Committee of the Shipping Transport & Logistics at the Bombay Chamber of Commerce & Industry (BCCI) and Director, Accex Supply Chain said, “The National Logistics policy, digital and technological advances have proved good for Industry. Sagaramala has boosted the infrastructural development in our waterways. We need to now focus on continued infra development at the right places; leverage on technological advances, skill development and Sustainable opportunities.”

The event was also attended by Rajiv Jalota, Inland Revenue, IAS, Chairperson, Mumbai Port Authority, and Additional Charge, Directorate General (DG), Directorate General of Shipping. Mr. Jalota said, “National Logistics Portal Marine (NLP Marine) has achieved the goal of providing a platform with complete end to end logistics solutions to facilitate exporter, importer and service provider to exchange documents easily and transact business.”

Prof. Ganapati D.Yadav, Emeritus Professor of Eminence highlighted about ESG priorities to organizations value to chain model, as stakeholders and customers’ demands for sustainability continue to grow, business executives will be eager to make responsible environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investments and incorporate state-of-the-art technologies into their operations to facilitate sustainable supply chains.
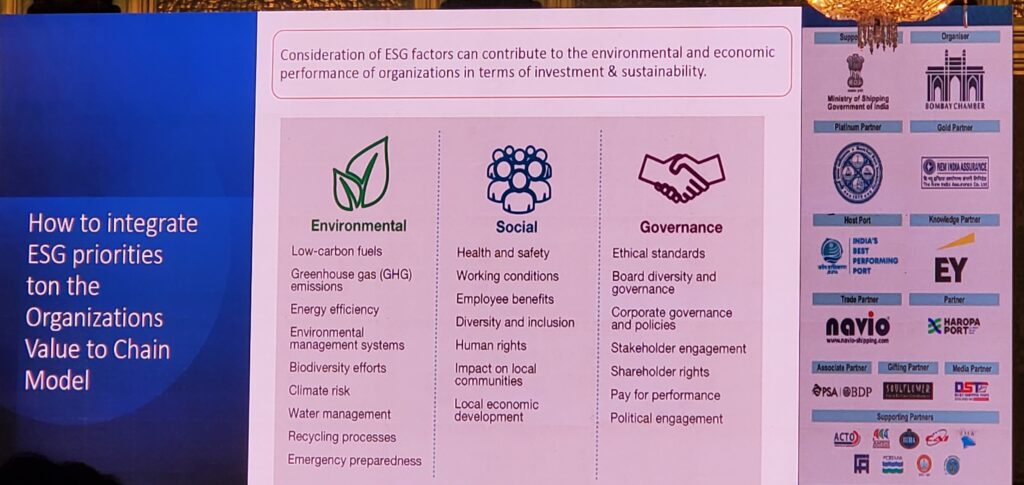
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations have become an essential part of the organization’s operations, and it is essential to involve employees in a meaningful way to embed the ESG framework in the organization and involve them in the strategic planning process.

The implementation of a sustainable supply chain is essential for any organization to reach its sustainability objectives, and an increasing number of companies are taking advantage of technology to achieve this goal. Deep technologies such as Cloud computing, AI, ML, and Analytics are helping businesses to optimize their logistics processes and consolidate all data into a single platform, thereby streamlining operations and increasing visibility.
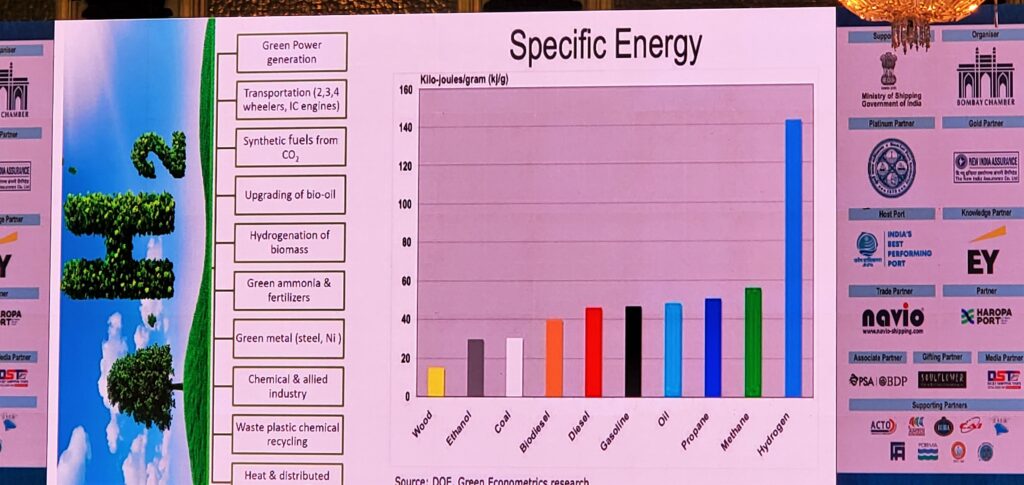
The ‘new trinity’ will be solar, wind and hydrogen, and hydrogen will be the key to reaching the net zero goal. It’ll also provide us with by-products like chemicals and materials made from biomass, including waste and plastic. What’s interesting is that in the future, refineries will be using carbon dioxide to make chemicals, polymers and materials, not crude oil, which is expected to run out by 2050.
India should adopt the hydrogen economy as it will increase its energy security and reduce greenhouse gas emissions and meet its obligations under the Paris Agreement. Hydrogen burns clean and produces only water. The traditional coal and oil based economy for the production of fuel, chemicals and raw materials is unsustainable and has caused significant damage to the environment.
The renewable energy share will increase from current ~27% to ~51% by 2035, to 13–24% by 2050, at ~ 8% CAGR at the mid-point, with an estimated investment of USD 150 billion by 2030 is predicted.
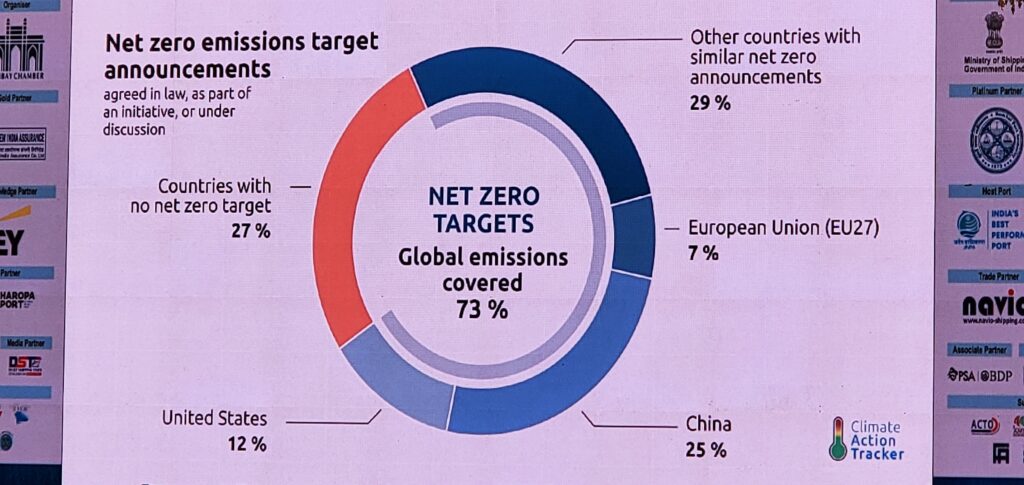
In a net-carbon-neutral economy, green hydrogen not only meets the goal of converting carbon dioxide into fuels and chemicals, but also converts waste biomass and waste plastic into fuels and chemicals.
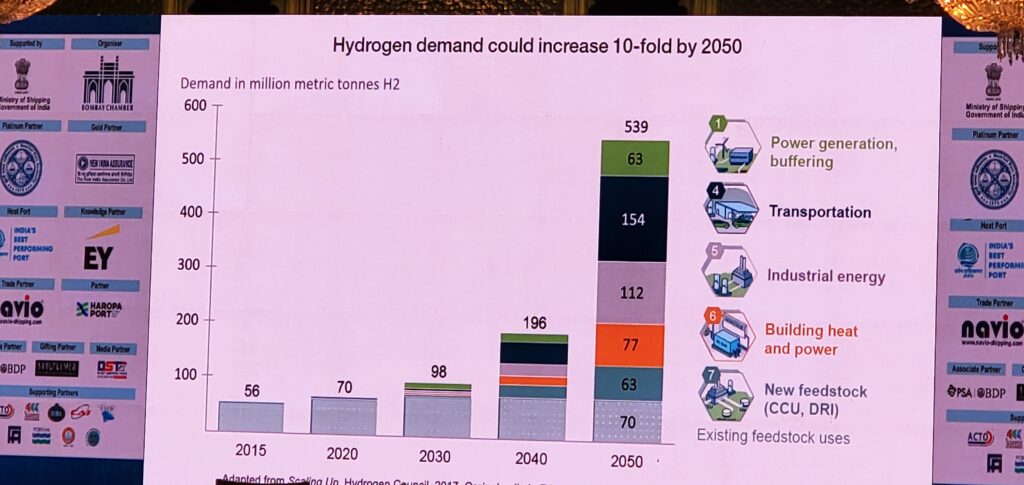
In order for hydrogen to play a role in mitigating climate change and achieving climate neutrality, its production must reach a much greater scale and be entirely produced through water splitting through green technologies.
The hydrogen economy faces a number of challenges to overcome, including the need for extensive infrastructure for hydrogen refilling stations, similar to petrol, diesel, and natural gas refuelling stations, and the need for low costs for hydrogen production, transportation, and storage. The Government should take the initial steps to meet its ambitious goals to achieve the 5 trillion dollar economy.

